If you’re using GoHighLevel for your business, connecting your Google Calendar is a must for ensuring your schedule is always up to date. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of integrating your Google Calendar with GoHighLevel so that you can manage your appointments effortlessly and prevent any scheduling conflicts.
Step 1: Accessing Calendar Settings
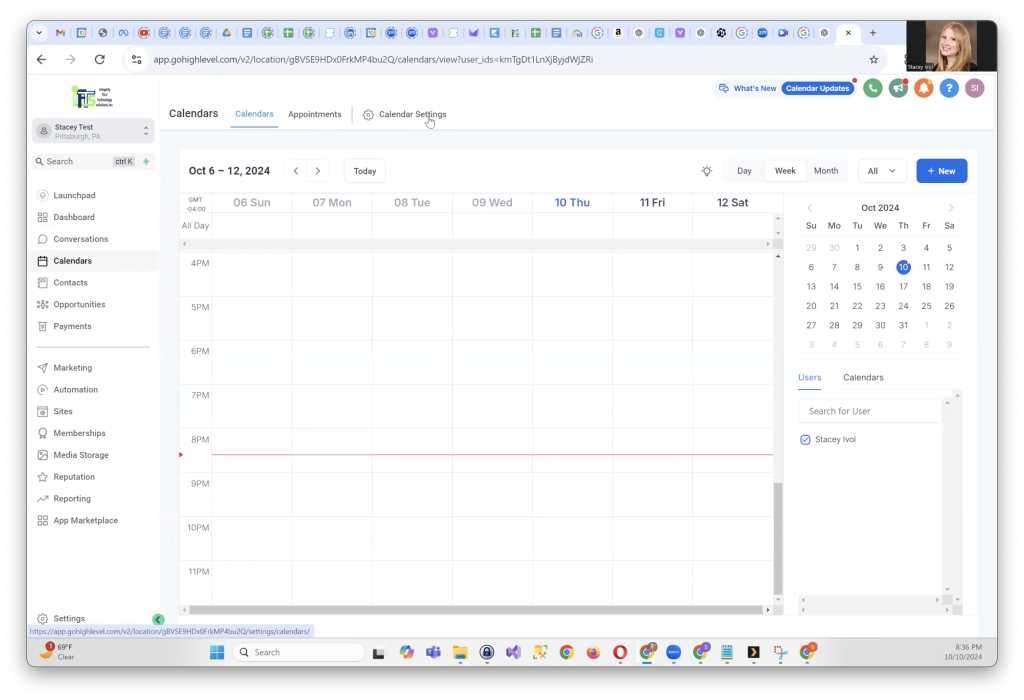
First, log into your GoHighLevel account. On the left-hand menu, click on Calendars, then select Calendar Settings from the upper menu. Here, you will see your current calendar setup.
You might notice open slots in your calendar, which will soon be synced and updated automatically once you connect your Google Calendar.
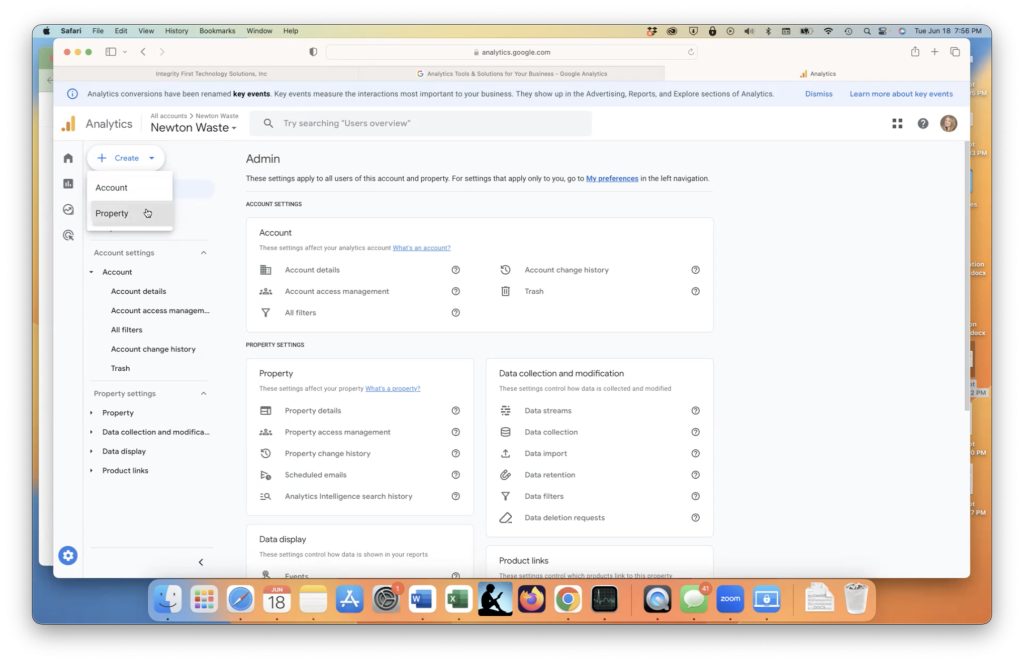
Step 2: Adding a New Calendar
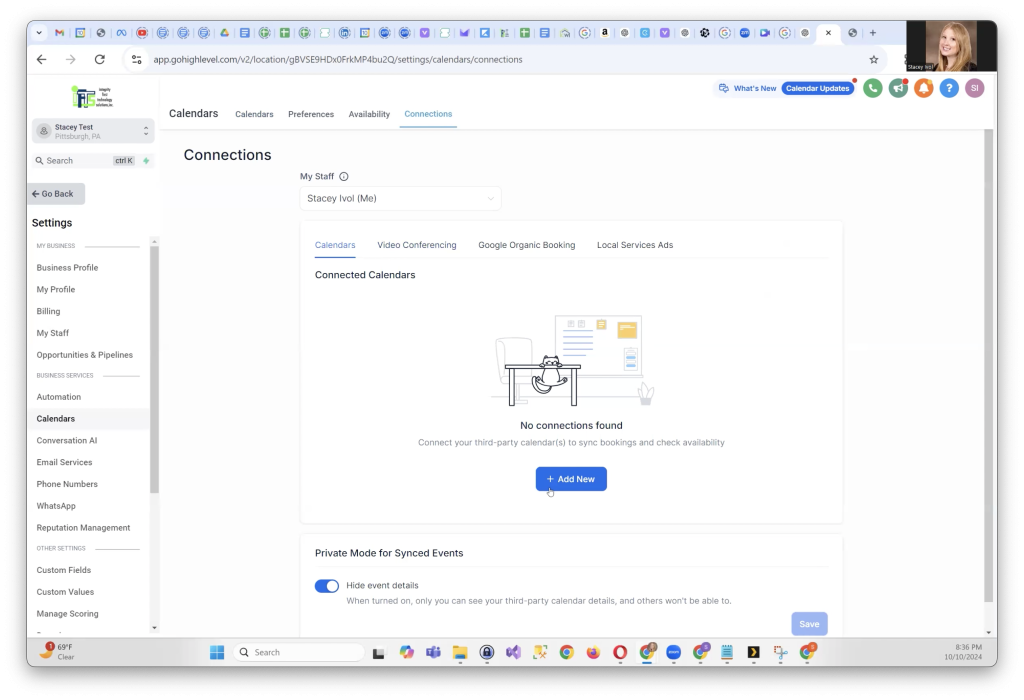
In the upper menu, click on Connections. Under the Calendars section, click on Add New. Now, choose Google Calendar as the service you want to connect.
Step 3: Signing in with Google
You’ll be prompted to sign in with your Google account. Select the account that you want to sync with GoHighLevel and click Continue.
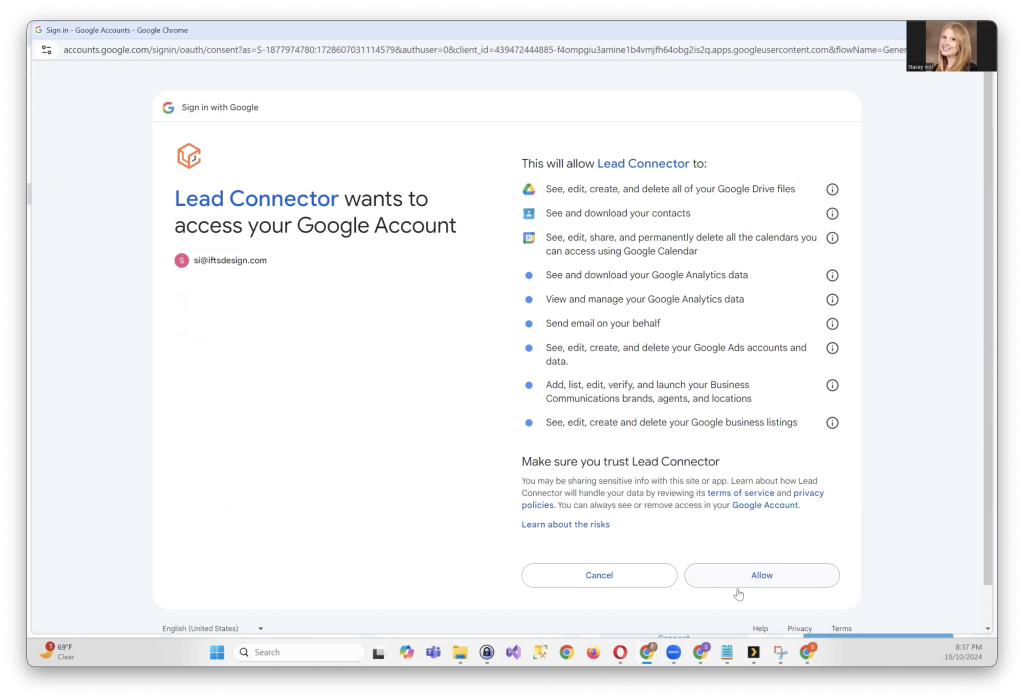
GoHighLevel uses a system called “Lead Connector” to sync with Google. When asked, click on Allow to complete the connection.
Step 4: Checking Calendar Connections
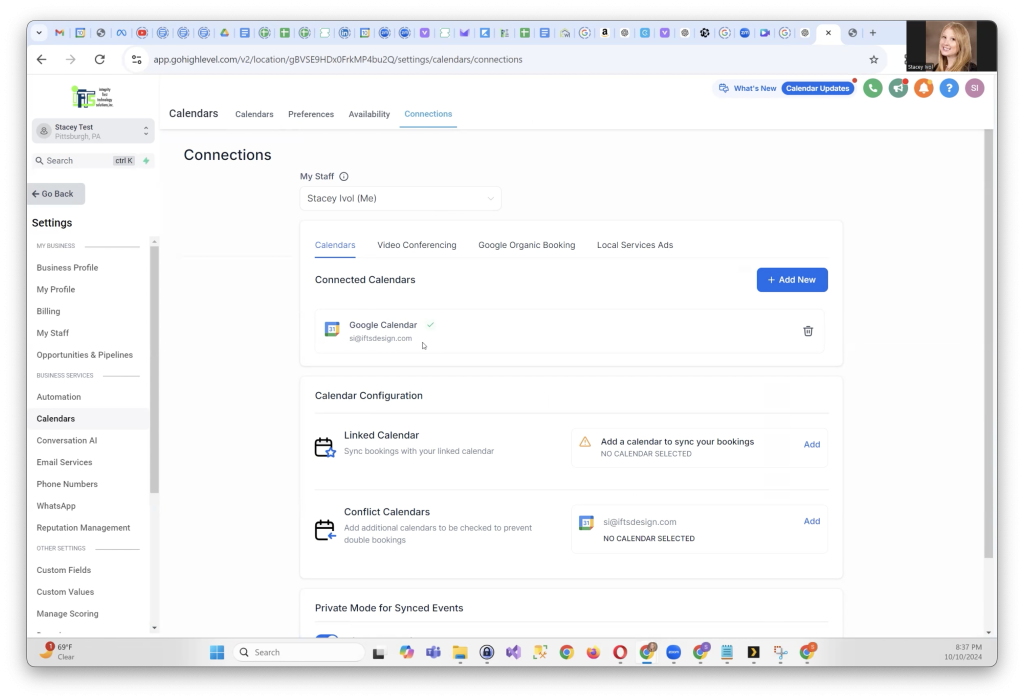
Although there isn’t an immediate confirmation, go back to Calendar Settings and click on Connections again. You should now see your Google Calendar listed as available.
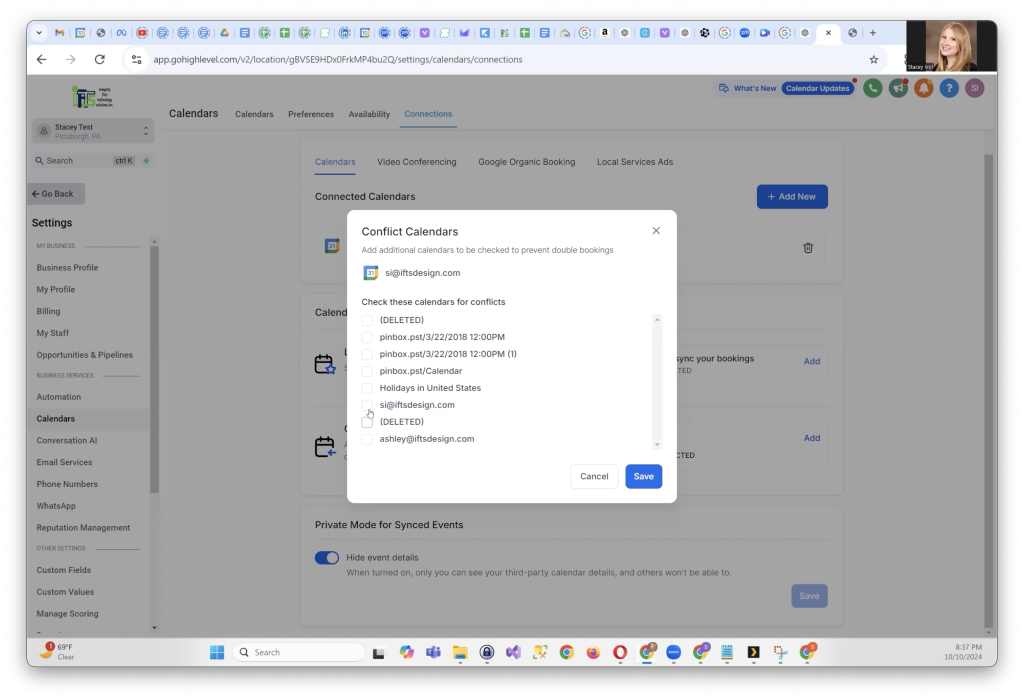
Step 5: Adding a Conflict Calendar
It’s crucial to set your connected Google Calendar as a Conflict Calendar to avoid double bookings. Select your Google Calendar from the list, name it (for example, “Google Calendar” or your company name), and click Save.
Step 6: Syncing Your Appointments
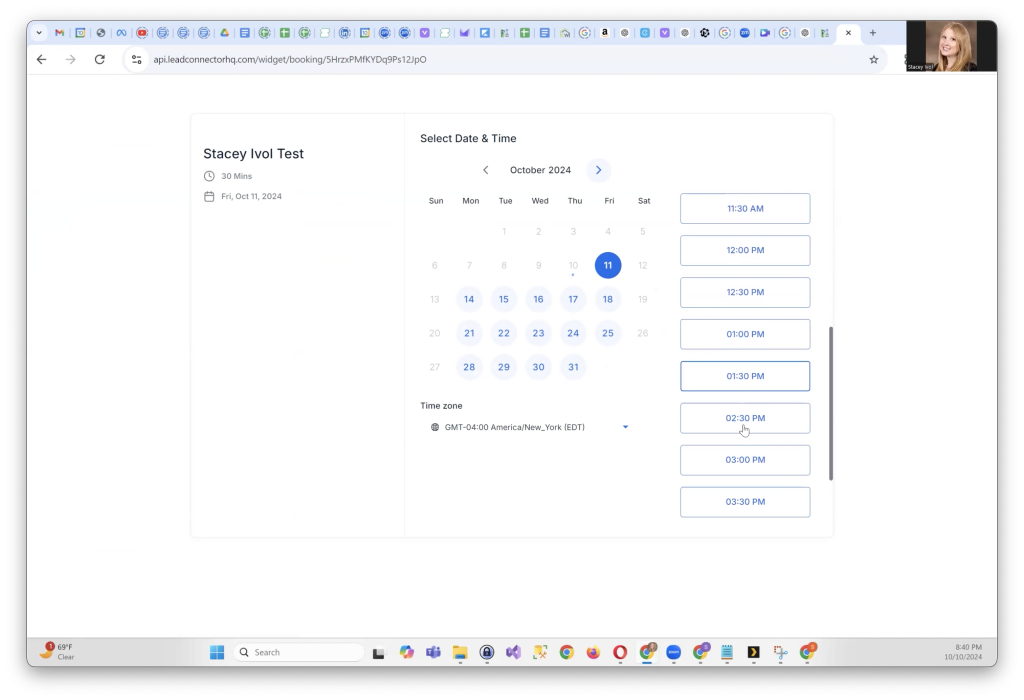
You’ll see a “processing” status as the sync happens. If this seems to take a while, try refreshing the page to speed up the process. Once it’s done, you’ll see that GoHighLevel is now synced with your calendar. You can test this by checking your available slots—appointments should now reflect correctly in your calendar.
All Set and Ready to Schedule
Syncing your Google Calendar with GoHighLevel is a quick process that helps you stay on top of your appointments and prevents scheduling conflicts. Follow these steps, and you’ll have a fully integrated system for managing your schedule in no time!